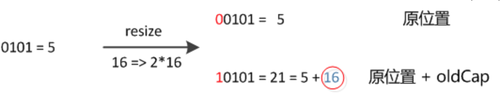HashMap 是 Java 中最重要的数据结构,也是最常用的集合类型。面试中基本都会问到一两个 HashMap 相关的问题。
由于 JDK 1.8 对 HashMap 进行了优化,基本上重写了 HashMap 的实现,所以通常还会考查 HashMap 的优化点。
本文收集整理了网上一些相关介绍,也是我在面试中常被问到的相关内容。
负载因子
loadFactor 负载因子,扩容机制的阈值,当超过了这个阈值,就会触发扩容机制。
- 值太大导致元素查找效率太低。当负载因子是 1.0 的时候,只有当数组的位置全部填充了才会发生扩容。会出现大量的 Hash 的冲突,底层的红黑树变得异常复杂,对于查询效率极其不利。
- 值太小数组的利用率过低,数据会很分散。
默认容量 16,loadFactor 0.75f。当数据达到 16 * 0.75 = 12 时,需要将当前容量扩容,涉及到 refresh 和复制数据,非常消耗性能。
扩容阈值:threshold = capacity * loadFactor
当数据量达到 threshold 时就需要对数组进行扩容,衡量数组是否需要扩增的一个标准。
JDK 1.7
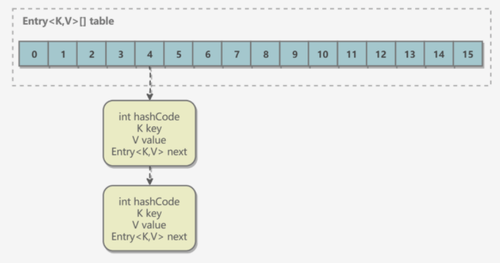
结构
Java 7 及之前的数据结构主要是由数组+链表组成。
PUT 操作
- 如果定位到的数组位置没有元素 就直接插入
- 如果定位到的数组位置有元素,遍历以这个元素为头结点的链表,依次和插入的 key 比较
- 如果 key 相同就直接覆盖,不同就采用头插法插入元素
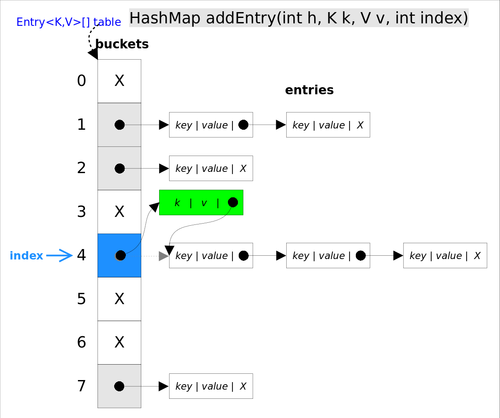
使用头插法插入元素,主要代码逻辑如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = hash & (table.length-1);
}
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
|
头插法会导致链表成环的问题。应避免在多线程下使用 HashMap。
GET 操作
get(Object key) 方法根据指定的 key 值返回对应的 value。
该方法调用了 getEntry(Object key) 得到相应的 entry,然后返回 entry.getValue()。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
......
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[hash&(table.length-1)];
e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}
|
算法思想是:
- 首先通过
hash() 函数得到对应 bucket 的下标
- 然后依次遍历冲突链表,通过
key.equals(k) 方法来判断是否是要找的那个 entry。
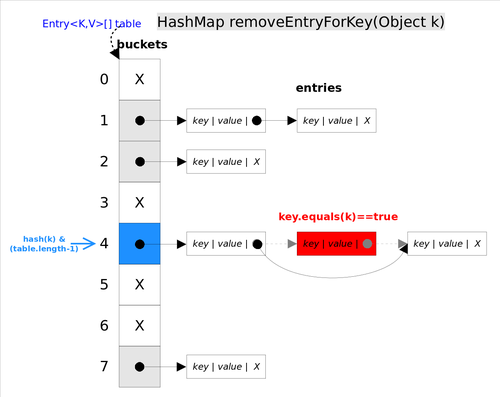
删除操作
删除方法的具体逻辑是在 removeEntryForKey(Object key) 里实现的。
removeEntryForKey() 方法会首先找到 key 值对应的 entry,然后删除该 entry(修改链表的相应引用)。查找过程跟 getEntry() 过程类似。
扩容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
transfer(newTable);
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
}
|
transfer() 方法将原有 Entry 数组的元素拷贝到新的 Entry 数组里。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| void transfer(Entry[] newTable) {
Entry[] src = table;
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (int j = 0; j < src.length; j++) {
Entry<K,V> e = src[j];
if (e != null) {
src[j] = null;
do {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
} while (e != null);
}
}
}
|
newTable[i] 的引用赋给了 e.next,也就是使用了单链表的头插入方式,同一位置上新元素总会被放在链表的头部位置。先放在一个索引上的元素终会被放到 Entry 链的尾部。
旧数组中同一条 Entry 链上的元素,通过重新计算索引位置后,有可能被放到了新数组的不同位置上。
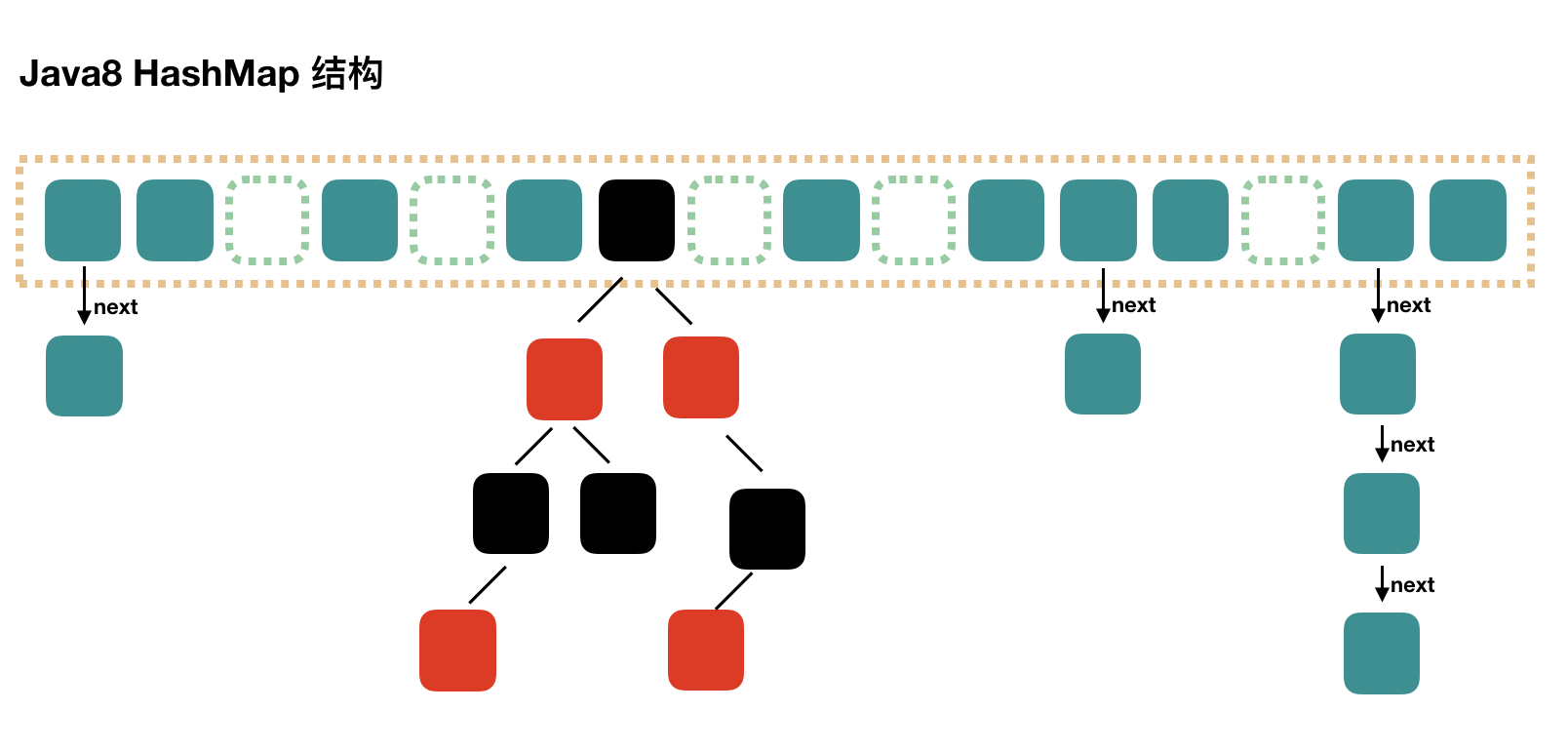
JDK 1.8
结构
由数组+链表/红黑树组成。
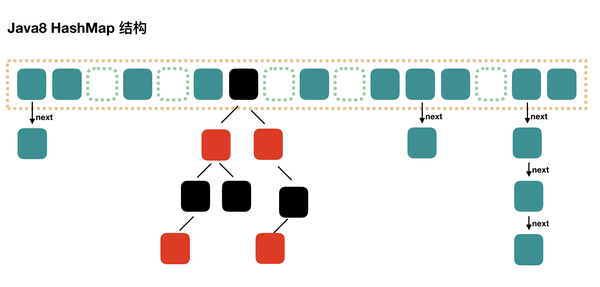
Java 7 HashMap 根据 hash 值能够快速定位到数组的具体下标,但是之后,需要顺着链表一个个比较下去才能找到需要的,时间复杂度取决于链表的长度,为 **O(n)**。
在 Java 8 中,当链表中的元素达到一定个数时,会将链表转换为红黑树,在这些位置进行查找的时候可以降低时间复杂度为 **O(logN)**。
当链表长度大于阈值(默认为 8):
- 如果数组长度小于 64 则先进行数组扩容
- 大于则将链表转化为红黑树,以减少搜索时间
PUT 操作
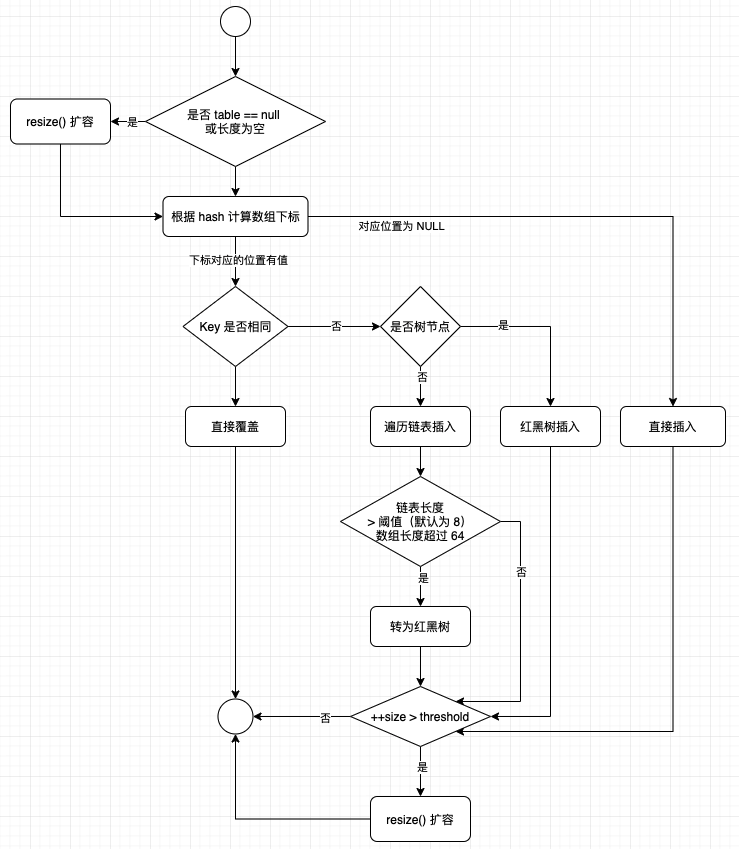
代码思想为:
- 如果定位到的数组位置没有元素就直接插入
- 如果定位到的数组位置有元素就和要插入的 key 比较
- 如果 key 相同就直接覆盖
- 如果 key 不相同,就判断 p 是否是一个树节点,如果是就调用红黑树插入
- 如果不是就遍历链表插入(插入的是链表尾部)
GET 操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first.hash == hash &&
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
|
代码思想为:
- 计算 key 的 hash 值,根据 hash 值找到对应数组下标:
hash & (length-1)
- 判断数组该位置处的元素是否刚好就是我们要找的,如果不是,走第三步
- 判断该元素类型是否是 TreeNode,如果是,用红黑树的方法取数据,如果不是,走第四步
- 遍历链表,直到找到相等(==或 equals)的 key
删除操作
HashMap 的删除操作并不复杂,仅需三个步骤即可完成:第一步是定位桶位置,第二步遍历链表并找到键值相等的节点,第三步删除节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| public V remove(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ?
null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
node = p;
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
if (p instanceof TreeNode)
node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
if (node instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
else if (node == p)
tab[index] = node.next;
else
p.next = node.next;
++modCount;
--size;
afterNodeRemoval(node);
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
|
第三步删除节点代码说明:
- 如果 node 是 TreeNode 类型,说明是红黑树,调用红黑树删除方法
- 如果删除的是第一个节点:
node == p,则指向下一节点
- 否则是链表,且 p 是前节点,node 是要删除的当前节点(链表,删除元素 node)
扩容
resize() 方法用于初始化数组或数组扩容,每次扩容后,容量为原来的 2 倍,并进行数据迁移。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
| final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1;
}
else if (oldThr > 0)
newCap = oldThr;
else {
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else {
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
|
新数组两条链表的位置
经过观测可以发现,HashMap 使用的是 2 次幂的扩展(指长度扩为原来 2 倍),所以元素的位置要么是在原位置,要么是在原位置再移动 2 次幂的位置。
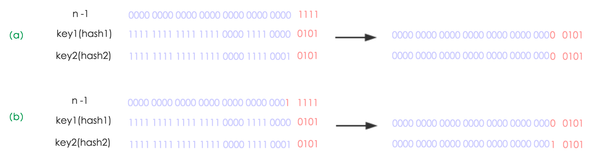
n 为 table 的长度:
- 图(a)表示扩容前的 key1 和 key2 两种 key 确定索引位置的示例
- 图(b)表示扩容后key1 和 key2 两种 key 确定索引位置的示例
元素在重新计算 hash 之后,因为 n 变为 2 倍,那么 n-1 的 mask 范围在高位多 1bit(红色),因此新的 index 就会发生这样的变化:
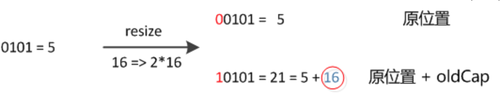
在扩充 HashMap 的时候,不需要像 JDK1.7 的实现那样重新计算 hash,只需要看看原来的 hash 值新增的那个 bit 是 1 还是 0 就好了:
- 0 的话索引没变
- 1 的话索引变成:
原索引 + oldCap
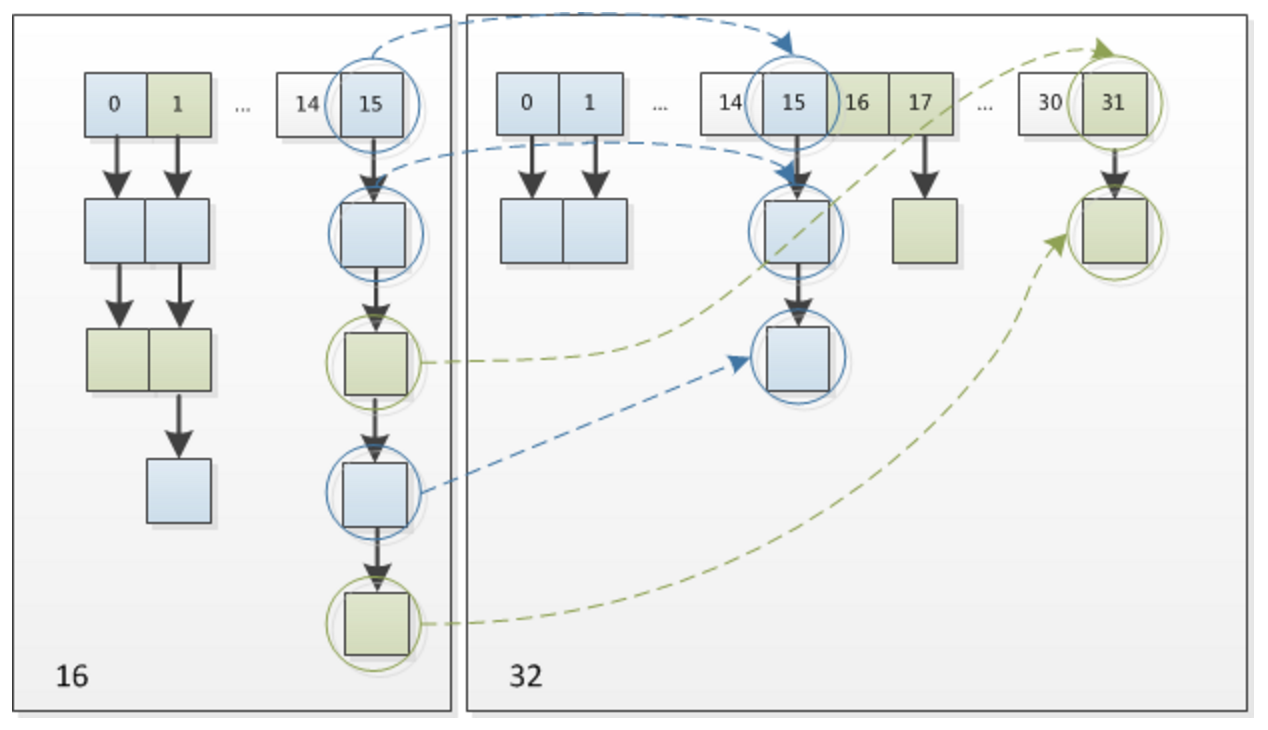
JDK1.7 中 rehash 的时候,旧链表迁移新链表的时候,如果在新表的数组索引位置相同,则链表元素会倒置,JDK1.8 不会倒置。
引用
- Map - HashSet & HashMap 源码解析
- HashMap 源码详细分析(JDK1.8)
- Java 8 系列之重新认识 HashMap